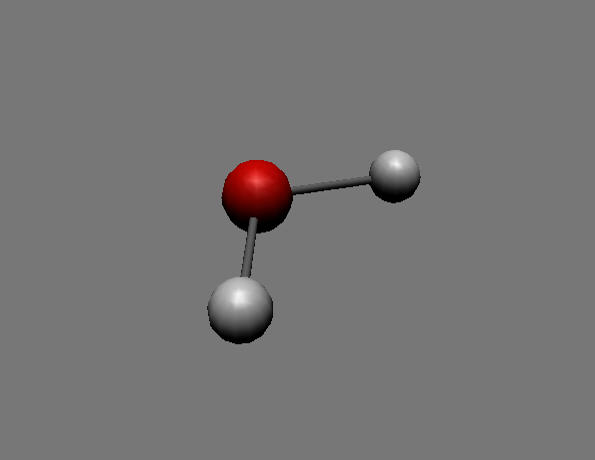
Water molecule
Water molecule
TLF ID R6843
This is a colour image of a model of a molecule of water, H₂O. In this model, atoms are represented by coloured spheres held together by grey rods, representing covalent bonds. The water molecule contains one oxygen atom (the red sphere) and two hydrogen atoms (the grey-white spheres).